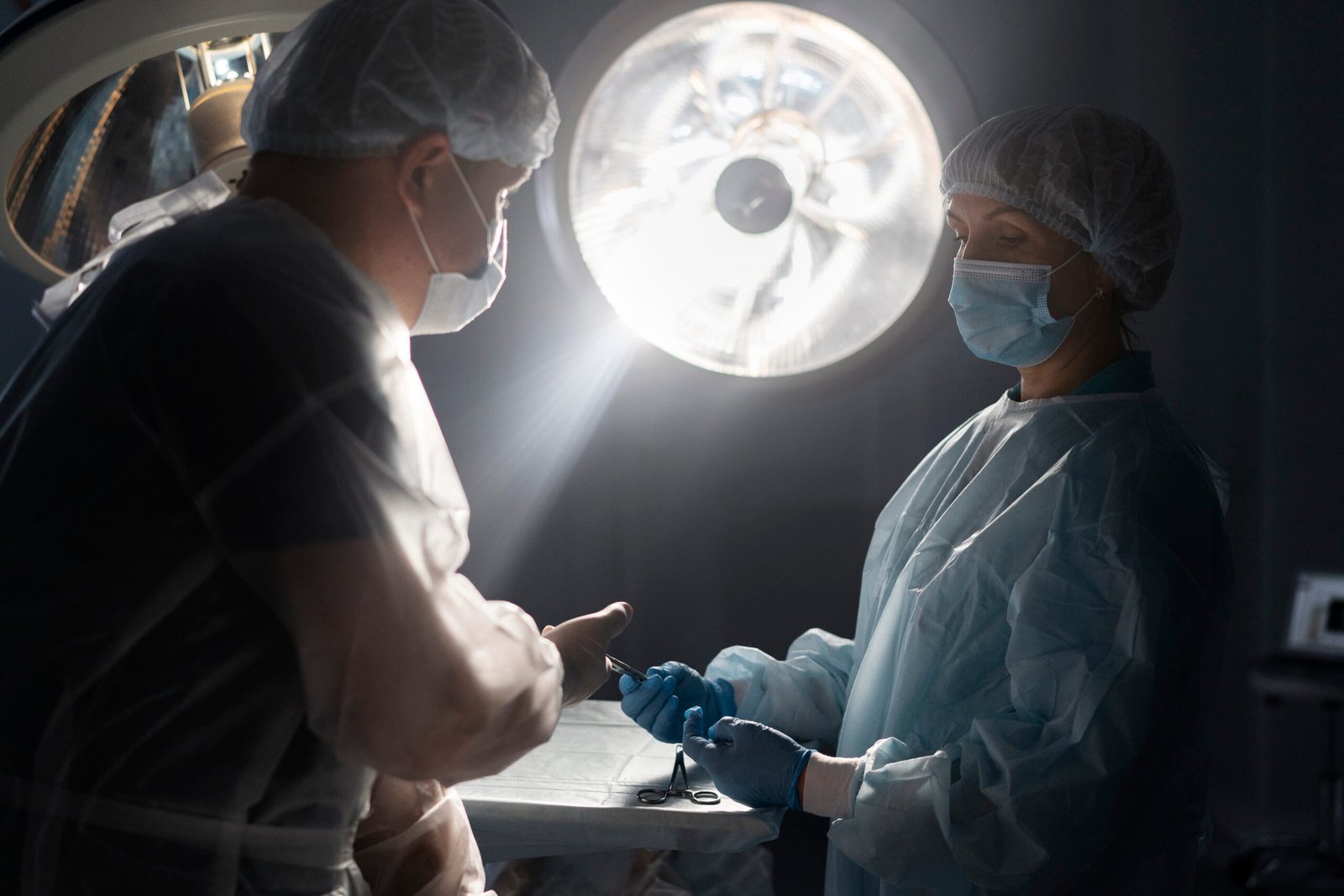
Introduction
Rib fractures are a common injury that can occur due to various reasons, from sports injuries and falls to car accidents. While many heal naturally without the need for surgical intervention, some cases may present complexities requiring careful consideration. In this article, we will explore the anatomy of rib fractures, the circumstances under which surgery may not be advisable, and the alternatives available for effective management. Understanding these aspects can help patients and caregivers make informed decisions about treatment options.
The Anatomy of Rib Fractures
What are They?
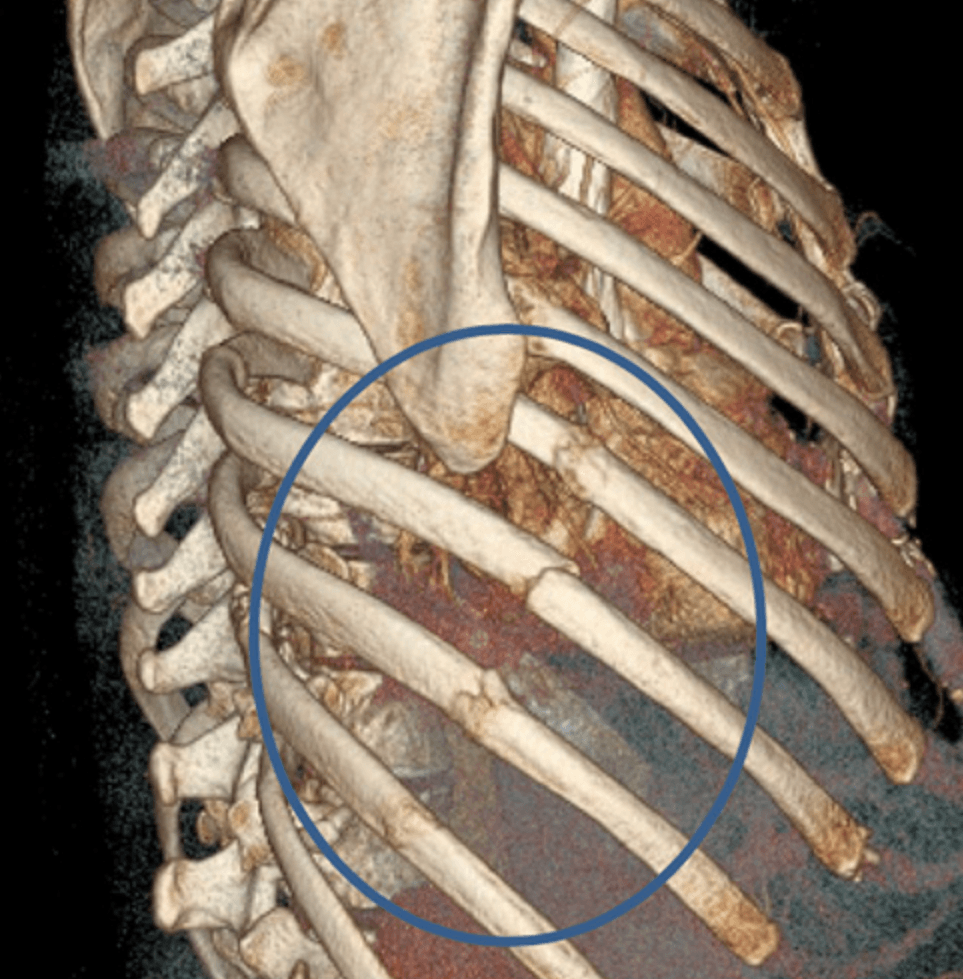
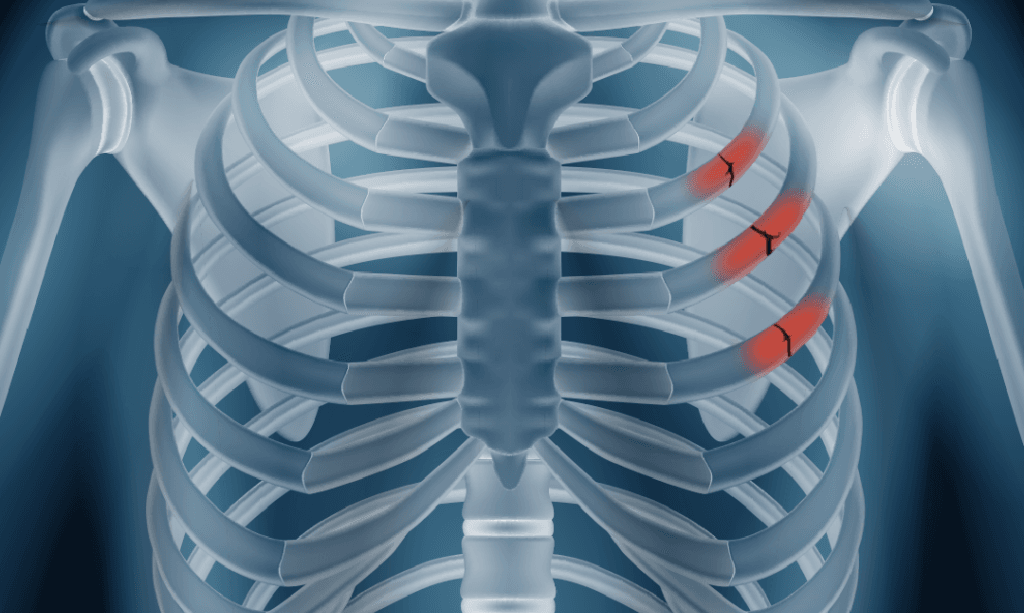
Rib fractures refer to breaks in one or more of the ribs, which are the bones that form the rib cage. The rib cage serves as a protective structure for vital organs, including the heart and lungs. Each rib is connected to the spine at the back and curves around to the front, where it attaches to the sternum. Fractures can be classified based on their type and severity, ranging from simple cracks in the rib bone to more complex breaks that may cause displacement or interference with the thoracic structures.
Common Causes
The primary causes of rib fractures include traumatic incidents such as falls, sports injuries, and vehicle collisions. Osteoporosis, a condition that weakens bones, can also lead to rib fractures from minor falls. Additionally, individuals involved in high-impact sports such as rugby or football are at a greater risk due to the physical nature of these activities. Understanding the cause of the fracture is crucial, as it guides the treatment approach.
When Not to Operate on Rib Fractures
Non-Displaced Rib Fractures
Non-displaced rib fractures are those in which the broken ends of the rib remain aligned and have not moved out of their normal position. These fractures typically do not pose a significant risk to the surrounding organs and are often managed conservatively. Treatment for non-displaced fractures usually involves rest, pain management, and gradual return to normal activities as healing progresses. Surgical intervention in these cases is usually unnecessary, as the body can heal itself effectively.
Stable Rib Fractures
Similar to non-displaced fractures, stable rib fractures do not result in significant displacement and maintain structural integrity. They often cause mild to moderate pain but do not compromise lung function or other vital structures. For such fractures, a conservative approach is commonly adopted, focusing on monitoring the patient’s progress and managing discomfort, rather than resorting to surgery.
Underlying Health Conditions
Patients with certain health conditions, such as advanced age, chronic respiratory diseases, or clotting disorders, may not be ideal candidates for surgery. Surgical procedures can carry higher risks for these individuals due to factors such as anesthesia complications, longer recovery times, and the potential for postoperative infections. In these cases, non-surgical management strategies are usually favored to ensure patient safety.
Age and Recovery Considerations
Age plays a significant role in determining the right approach to treating rib fractures. Elderly patients, in particular, may have a slower healing response and a higher likelihood of complications during surgery. It is often recommended that older adults with rib fractures be treated conservatively, allowing time for natural healing while managing pain and other symptoms through medication and supportive care.
When to Consider Fixing Rib Fractures
Severe Chest Trauma
In some situations, rib fractures can be associated with severe chest trauma that compromises the integrity of the thoracic cavity or causes damage to internal organs. Examples include multiple rib fractures, flail chest, or fractures that puncture the lung. In these cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to stabilize the rib cage and prevent further complications, including respiratory distress.
Non-Union of Rib Fractures
Non-union occurs when a fractured rib fails to heal properly over an extended period, leading to persistent pain and functional limitations. This condition may necessitate surgical intervention, particularly if the patient experiences chronic discomfort or reduced lung capacity. Surgical options might include rib plating or fixation to promote healing and restore normal rib function, allowing for improved respiratory mechanics.
Rib Plating: An Overview
Rib plating is a modern surgical technique used to stabilize rib fractures. It involves the use of metal plates and screws that are attached to the rib bone, promoting proper alignment and healing. This surgical approach can be particularly beneficial for patients with multiple rib fractures or those who have ongoing pain despite conservative management. Rib plating can also improve lung function by allowing for better chest wall mechanics during breathing.
Benefits of Rib Fixation
Choosing surgical fixation for rib fractures can lead to several benefits, particularly for patients facing complications from their injuries. These benefits include reduced pain, improved lung function, and quicker recovery times. Furthermore, with stabilized ribs, patients are often able to resume normal activities and engage in rehabilitation sooner than with non-surgical approaches, contributing to a better overall quality of life.
Alternatives to Surgery
Pain Management Techniques
For many individuals with rib fractures, effective pain management is the cornerstone of treatment. This may involve the use of over-the-counter analgesics, prescription medications, or techniques such as nerve blocks to alleviate discomfort. Additionally, breathing exercises and the use of incentive spirometry can prevent complications like pneumonia by encouraging deep breaths, even in the presence of pain.
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in the recovery process for individuals with rib fractures. A structured rehabilitation program can help restore strength, flexibility, and range of motion following the injury. Therapists may also incorporate breathing exercises to promote lung expansion and reduce the risk of respiratory complications. Beginning physical therapy early in the recovery process, under professional guidance, can lead to better outcomes.
When to Seek Further Medical Advice
Patients should be vigilant about monitoring their symptoms and seeking further medical advice if they experience worsening pain, difficulty breathing, or any signs of infection, such as fever or increased cough. Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are essential to ensure that healing is progressing and to address any potential complications that may arise during recovery.
Conclusion
Rib fractures can be daunting, but understanding the nuances of treatment options can empower patients and their families. While many rib fractures heal without surgical intervention, specific circumstances warrant a more aggressive approach. By assessing factors like fracture type, underlying health conditions, and patient age, medical professionals can tailor treatment plans that prioritize safety and promote effective healing. For those opting against surgery, effective pain management and rehabilitation strategies remain vital components of recovery. Ultimately, informed choices lead to better outcomes and a return to normalcy.
FAQs
What are the symptoms of a rib fracture?
Common symptoms include sharp, localized pain in the chest area, difficulty breathing, bruising, and swelling. Patients may also experience pain during movement, coughing, or taking deep breaths.
How long does it take for a rib fracture to heal?
Most rib fractures typically heal within 6 to 8 weeks, depending on the severity of the fracture and the individual’s overall health. However, older adults or those with underlying health issues may require a longer recovery period.
Can I exercise with a rib fracture?
It is advisable to avoid strenuous activities and heavy lifting while healing from a rib fracture. Light activities and specific breathing exercises may be encouraged, but any exercise regimen should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
Are rib fractures serious?
While rib fractures can be painful, they are not always serious. However, complications can arise, particularly if the fracture is associated with damage to internal organs or if the patient has other underlying health conditions. It’s important to monitor symptoms and seek medical attention if necessary.
How can I manage pain from a rib fracture?
Pain management may include over-the-counter pain medications, prescription medications, or alternative therapies such as ice application and breathing exercises. Consulting a healthcare provider for personalized pain management strategies is crucial.