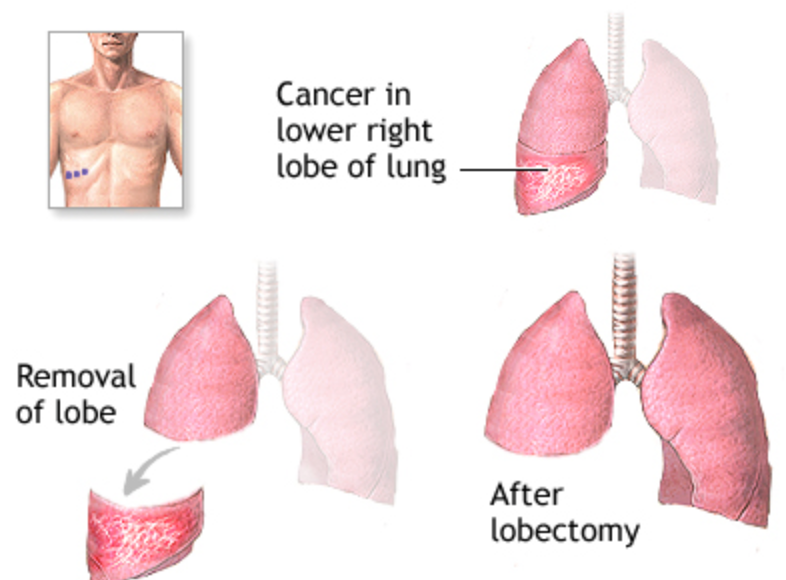
One of the most common thoracic surgeries is a lobectomy, which involves the removal of a lobe from the lung. This procedure is often performed to treat lung cancer or other conditions affecting the lung. Other common thoracic surgeries include thoracotomy, lung biopsy, and thoracoscopy. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for specific information related to individual cases.
What is a pulmonary lobectomy?
A lobectomy is a surgical procedure in which a lobe of an organ is removed. This procedure is commonly performed in the context of lung surgery, where a lobe of the lung is removed due to conditions such as cancer, infection, or severe lung damage. In the case of the lung, each lung has multiple lobes, and a lobectomy may involve the removal of one or more lobes depending on the extent of the disease or condition. It is a serious surgical procedure that should be discussed thoroughly with a healthcare provider.
What are the Indications for a Pulmonary Lobectomy?
A pulmonary lobectomy is a surgical procedure where one of the lobes of the lung is removed. Some of the common indications for a lobectomy include:
1. Lung cancer: Lobectomy is often performed as a treatment for early-stage lung cancer, particularly when the tumor is located in one lobe of the lung.
2. Lung infections: In cases where a severe infection such as a lung abscess or a fungal infection is localized to one lobe of the lung and does not respond to other treatments, a lobectomy may be necessary.
3. Benign lung tumors: Some non-cancerous lung tumors, such as pulmonary nodules or hamartomas, may require a lobectomy if they are causing symptoms or growing rapidly.
4. Bronchiectasis: This condition involves the permanent enlargement of the bronchial tubes due to chronic inflammation. If the affected area is localized to one lobe and causing significant symptoms, a lobectomy may be considered.
5. Lung damage or trauma: Severe lung damage from injuries or conditions like cystic fibrosis may sometimes necessitate the removal of a lobe of the lung to improve overall lung function.
It is important to note that the decision to perform a lobectomy is based on individual circumstances and should be discussed thoroughly with a healthcare provider.
Procedure Overview of pulmonary lobectomy
A pulmonary lobectomy is a surgical procedure in which a lobe of an organ is removed. This procedure is commonly performed on the lung, where a section of the lung that is diseased or affected is surgically removed. Lobectomy is often used to treat lung cancer, severe infections, or other conditions that affect the lung tissue.
During a pulmonary lobectomy, the surgeon makes an incision in the chest to access the lung and then removes the lobe containing the affected tissue. The remaining lobes of the lung are then able to expand and function to help the patient breathe adequately.
Lobectomy is a major surgical procedure that requires general anesthesia and typically involves a hospital stay for recovery. Before undergoing a lobectomy, patients will need to undergo various tests and evaluations to determine if they are suitable candidates for the surgery.
It is important to follow all pre-operative and post-operative instructions provided by the medical team to ensure a successful recovery and optimal outcomes.
What are the risks of a pulmonary lobectomy?
A pulmonary lobectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of a lobe of the lung. As with any surgery, there are risks and potential complications associated with a lobectomy. Some of the risks include:
1. Bleeding: There is a risk of bleeding during or after the surgery, which may require further intervention.
2. Infection: As with any surgical procedure, there is a risk of developing an infection at the incision site or in the lungs.
3. Pneumonia: Removing a lobe of the lung can increase the risk of developing pneumonia, a lung infection.
4. Air leakage: There is a possibility of air leakage from the lungs into the chest cavity, which may require a chest tube to drain the air.
5. Breathing difficulties: Some patients may experience temporary or even permanent breathing difficulties after a lobectomy.
6. Nerve damage: During surgery, there is a risk of damaging nerves that control various functions, such as the diaphragm or vocal cords.
7. Blood clots: There is a risk of developing blood clots in the legs (deep vein thrombosis) or lungs (pulmonary embolism) after surgery.
It’s important to discuss these risks with your healthcare provider before undergoing a lobectomy and to be aware of the potential complications. Your healthcare team will take steps to minimize these risks and provide you with the best possible care during and after the surgery.